Eugène Viollet-le-Duc
Le Massif du Mont Blanc
1868–1876
LE MASSIF DU MONT-BLANC
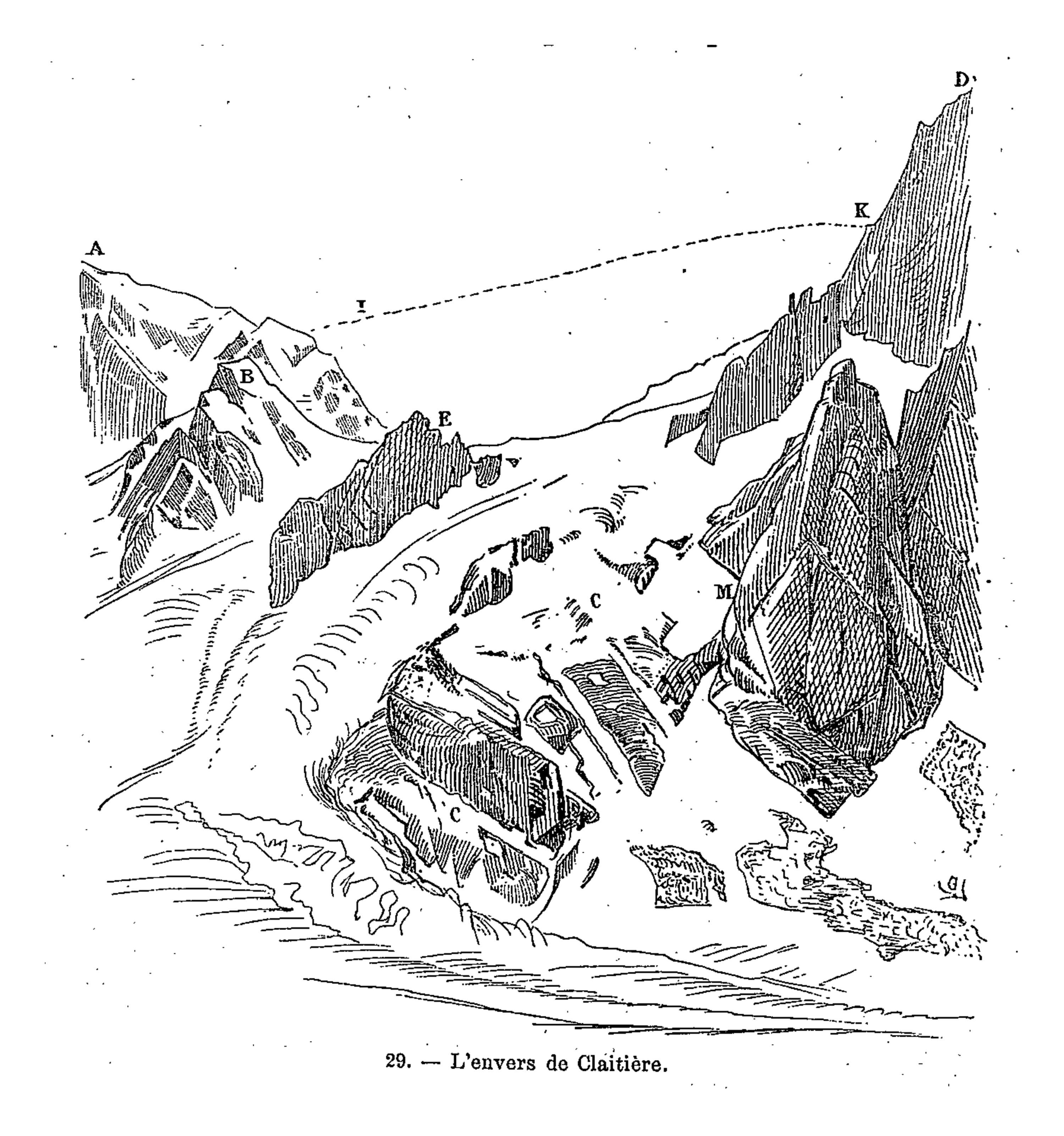
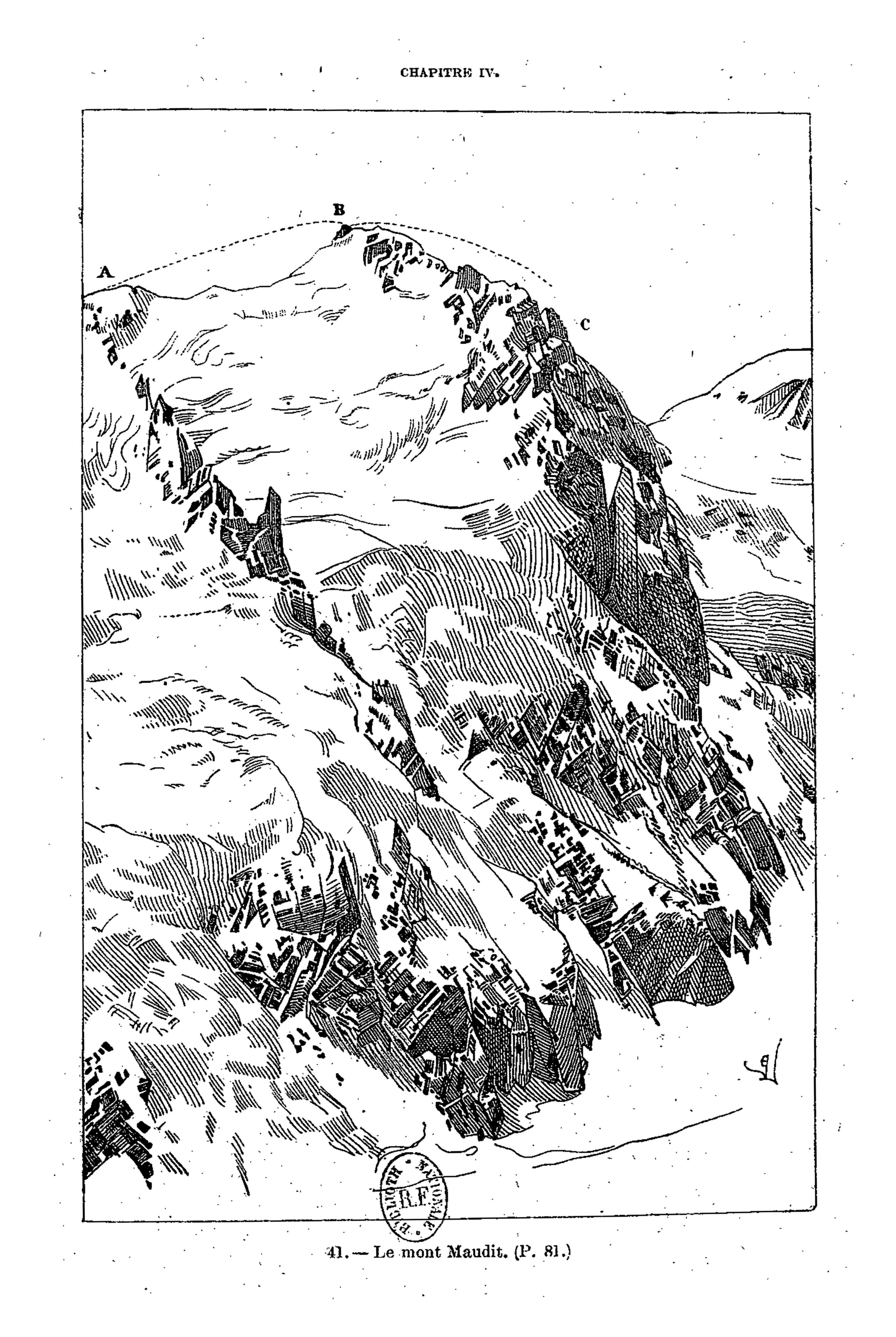
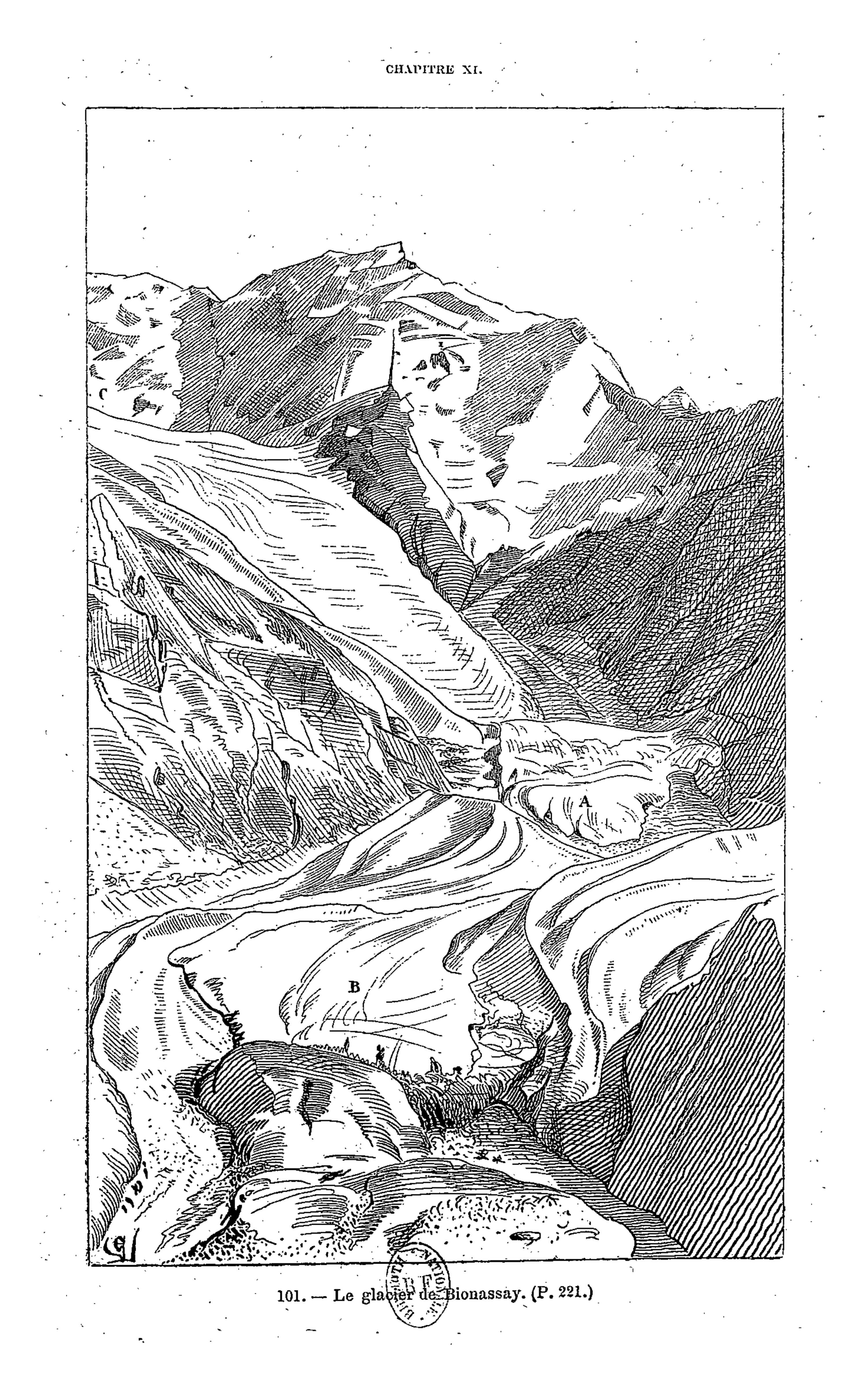
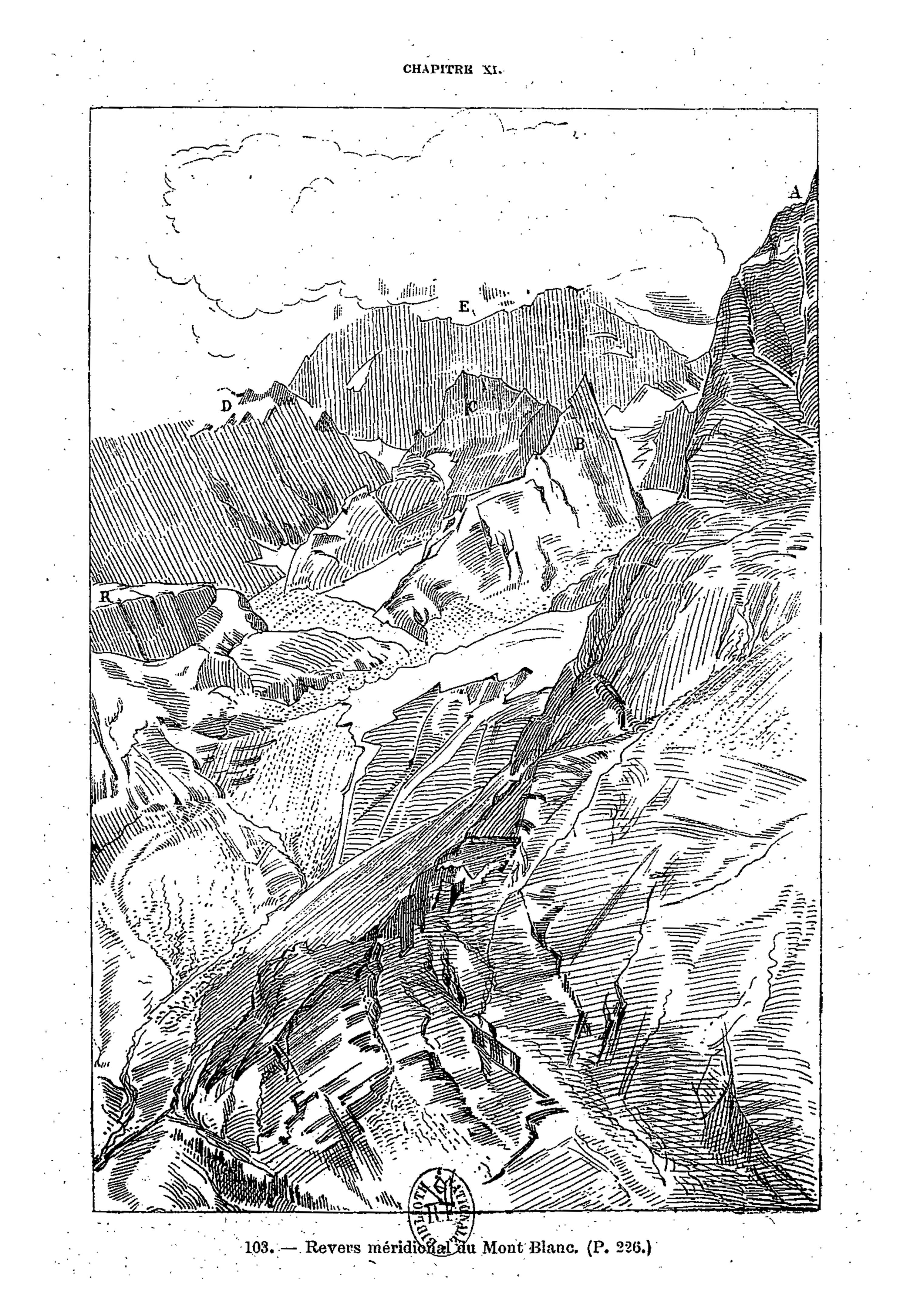
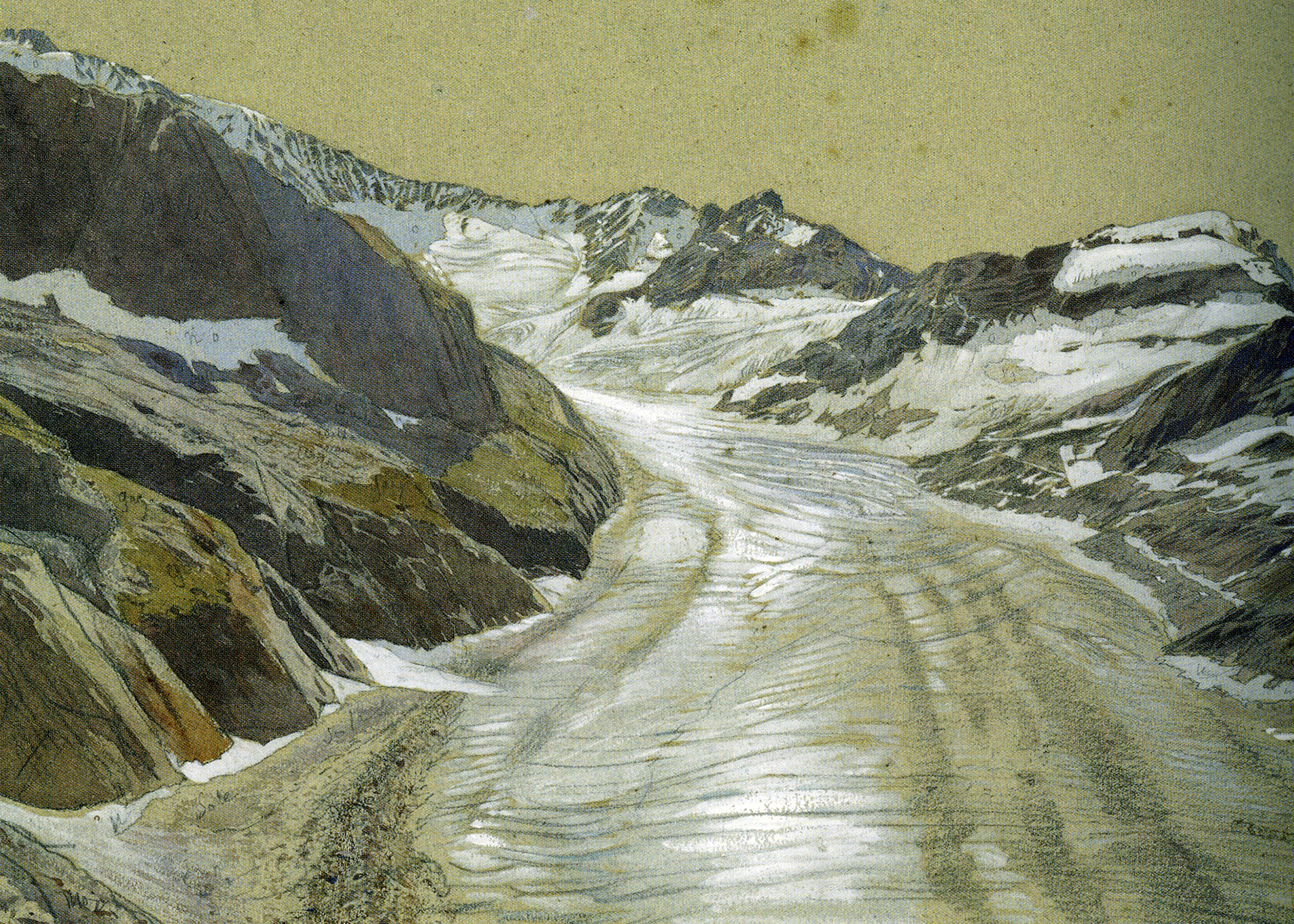
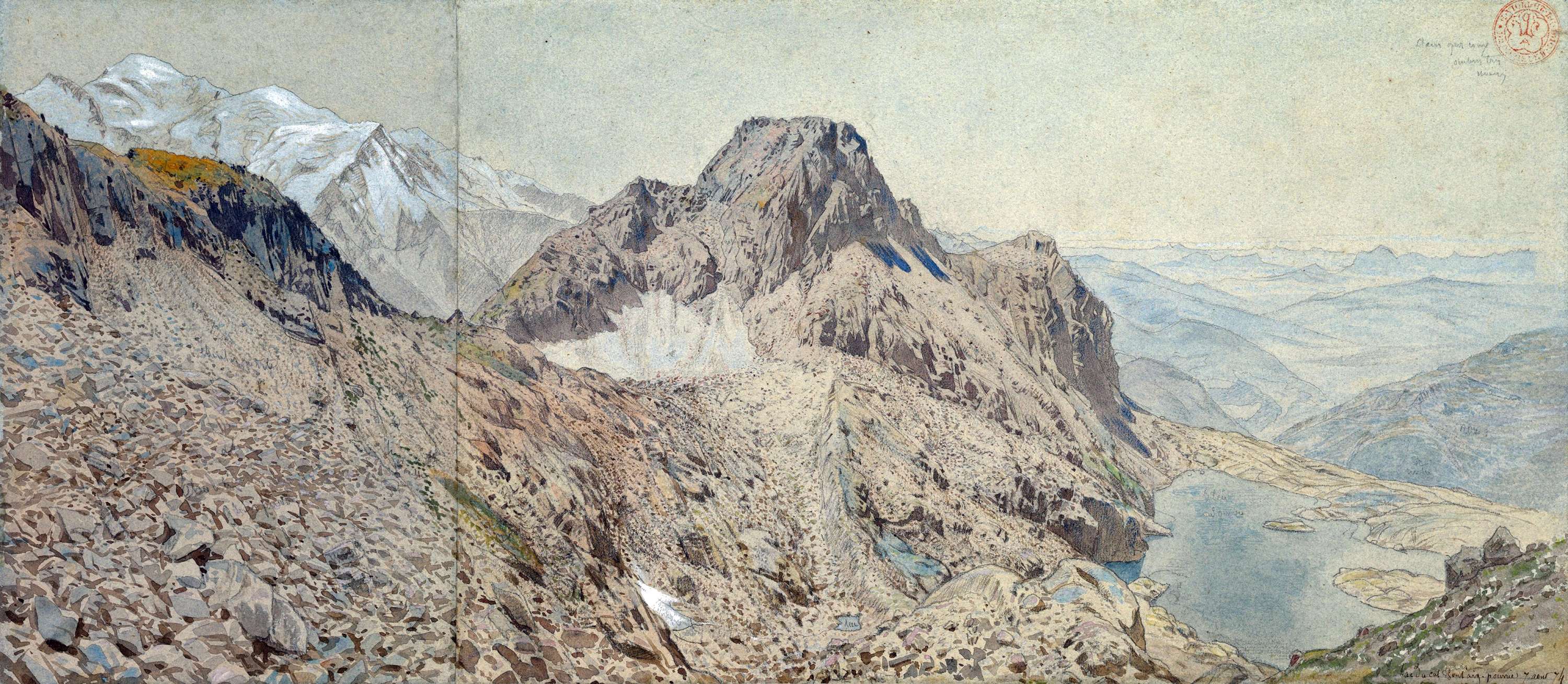
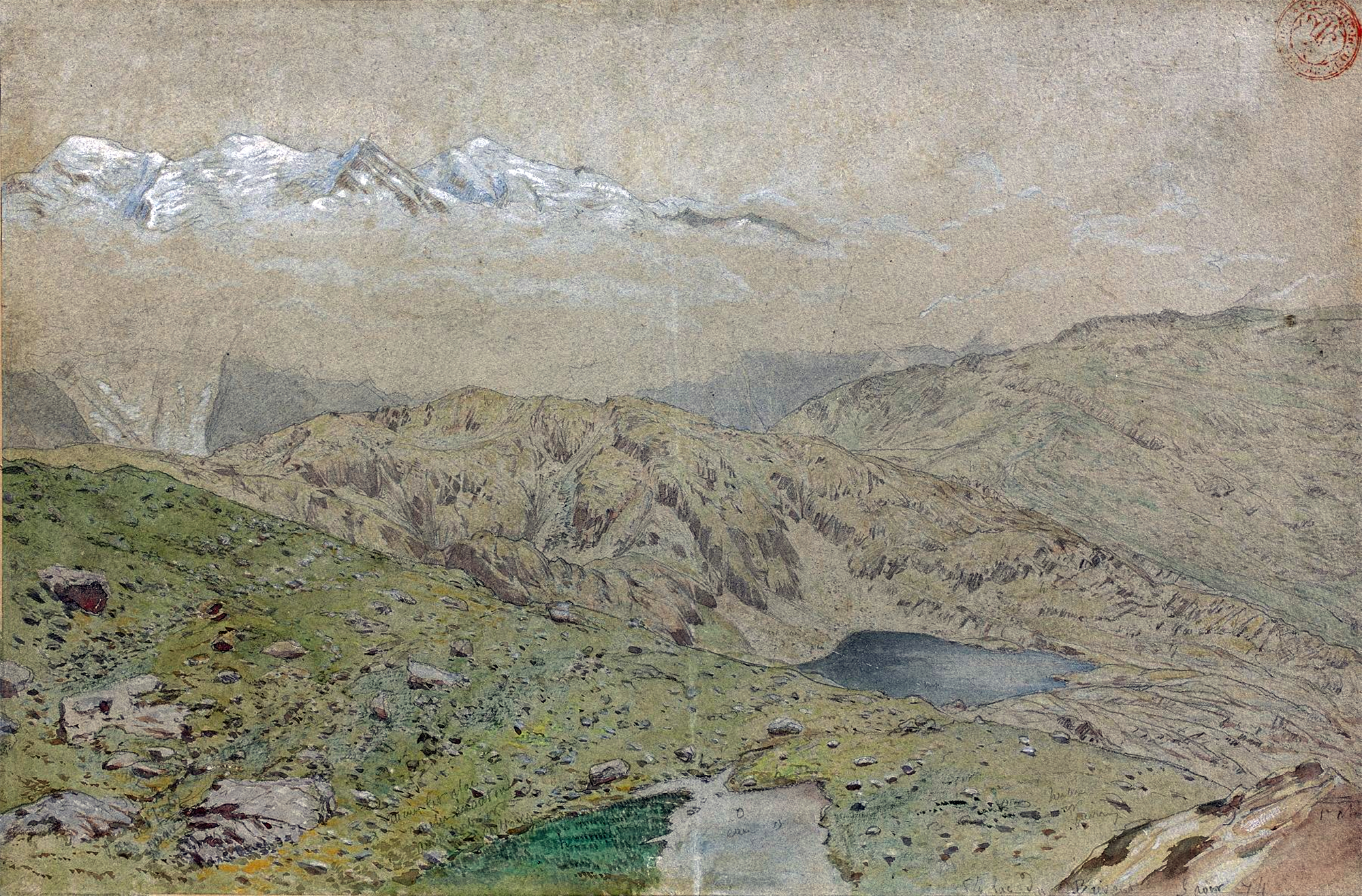
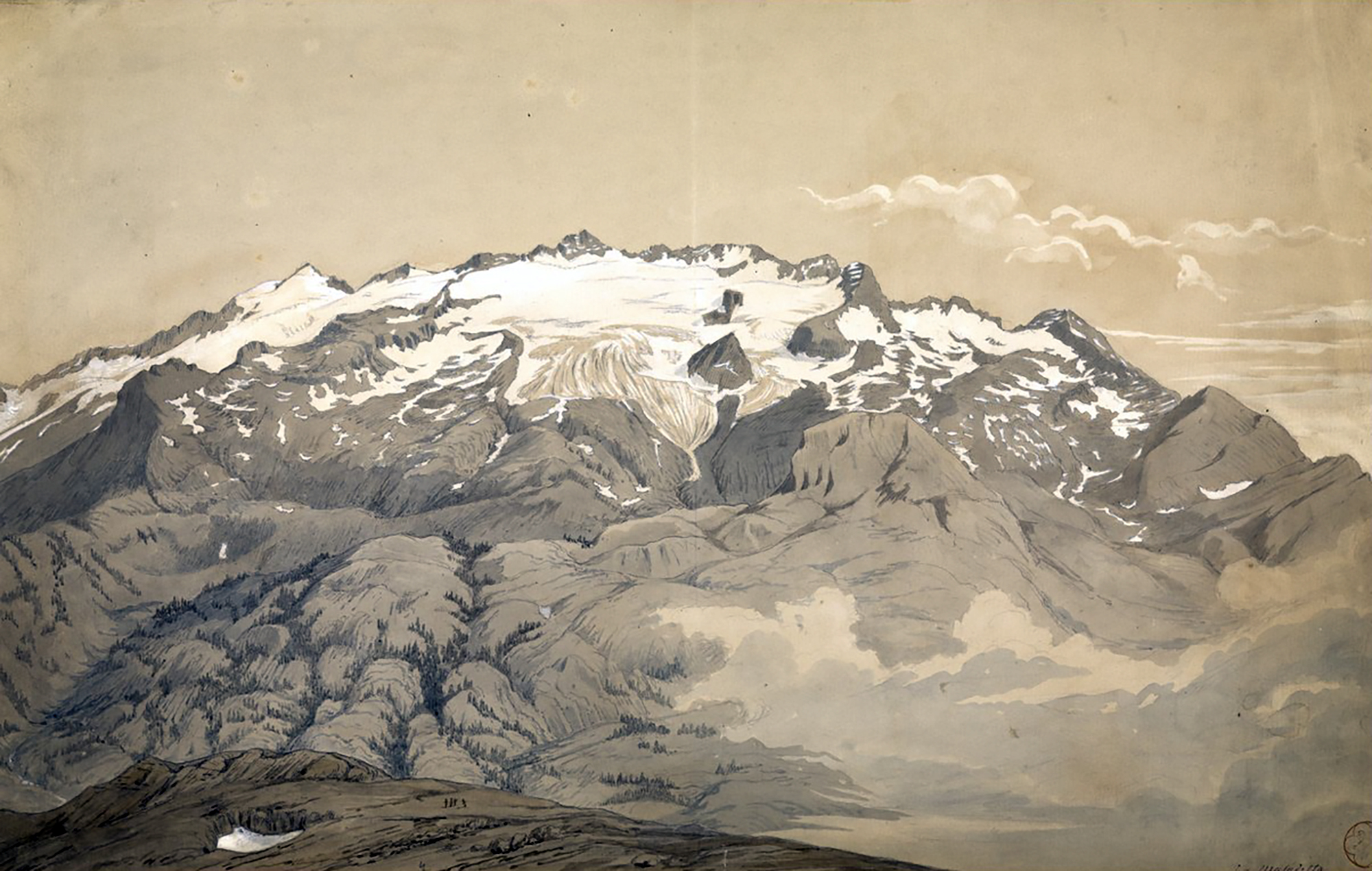
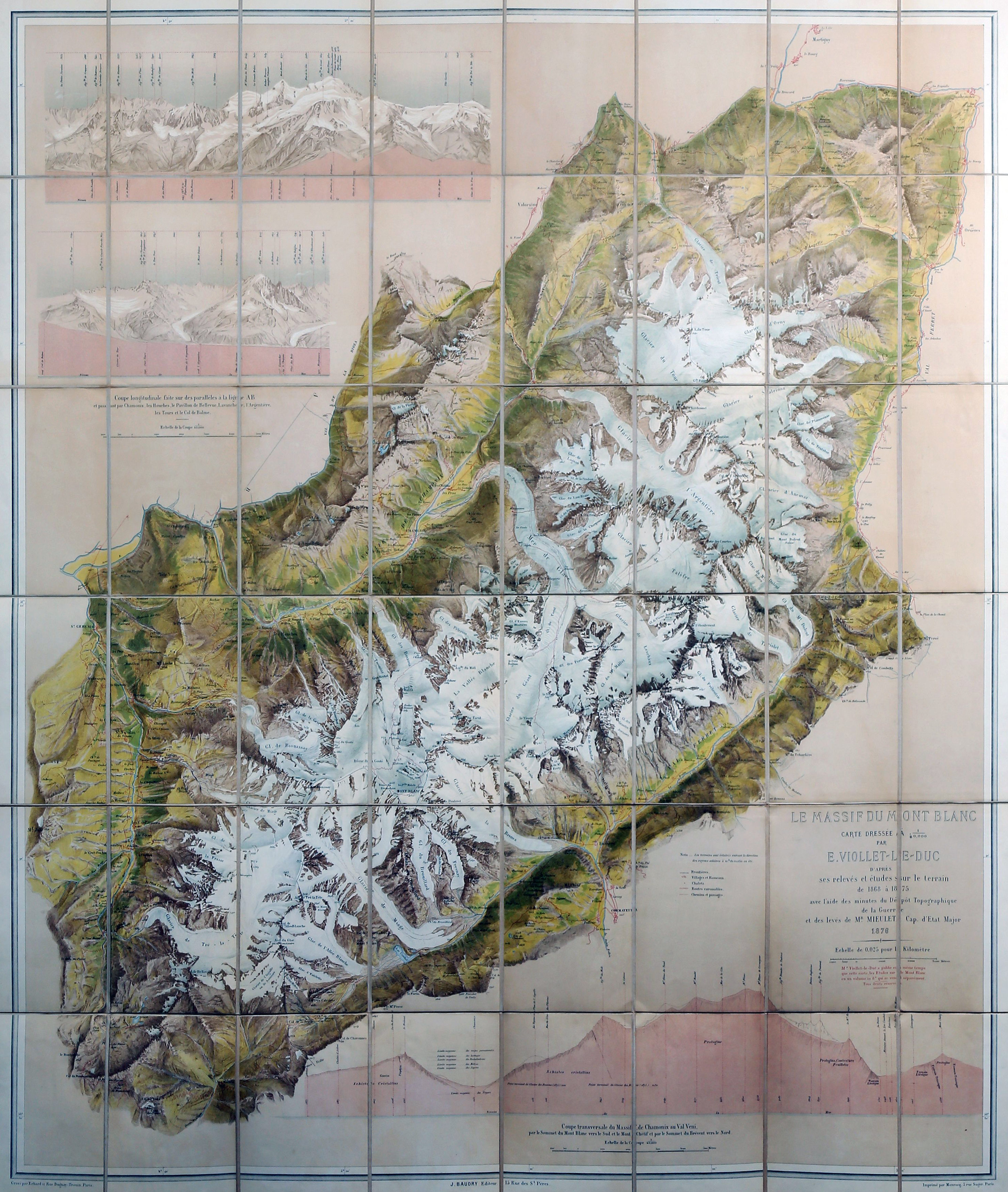
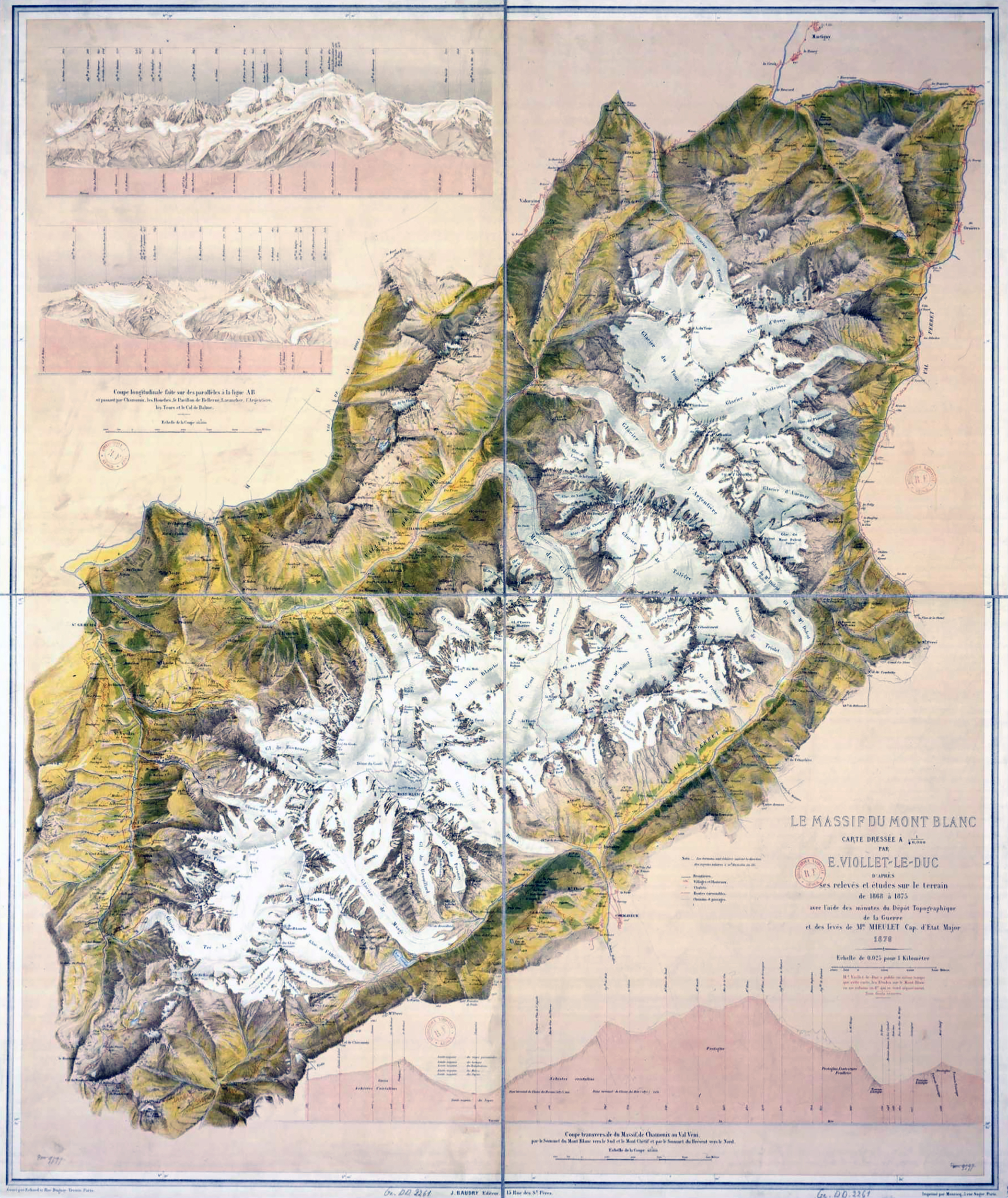
Viollet-le-Duc’s geological work follows closely from his work as medieval archeologist and architect. Having spent his life studying the play of structural forces that operate in buildings, whether medieval or modern, towards the end he passed to the contemplation of the same primary laws and forces working in nature on the grandest scale. For eight years between 1868 and 1876, he used his summer vacation to study and measure Mont Blanc, the greatest of European mountains. His first aim was the preparation of a complete and systematic map of the region under survey – a goal he achieved spectacularly with the production of a huge and stunning chromolithographic plan ‘view’ of the massif ‘as if it had been photographed from an altitude of 10’000 meters’. Thanks to a graphical method using subtly graduated light and shade, he could produce a vivid representation of the configuration of the slopes, with its hollows and recesses, and the sharp and abrupt contour of the mountain peaks.
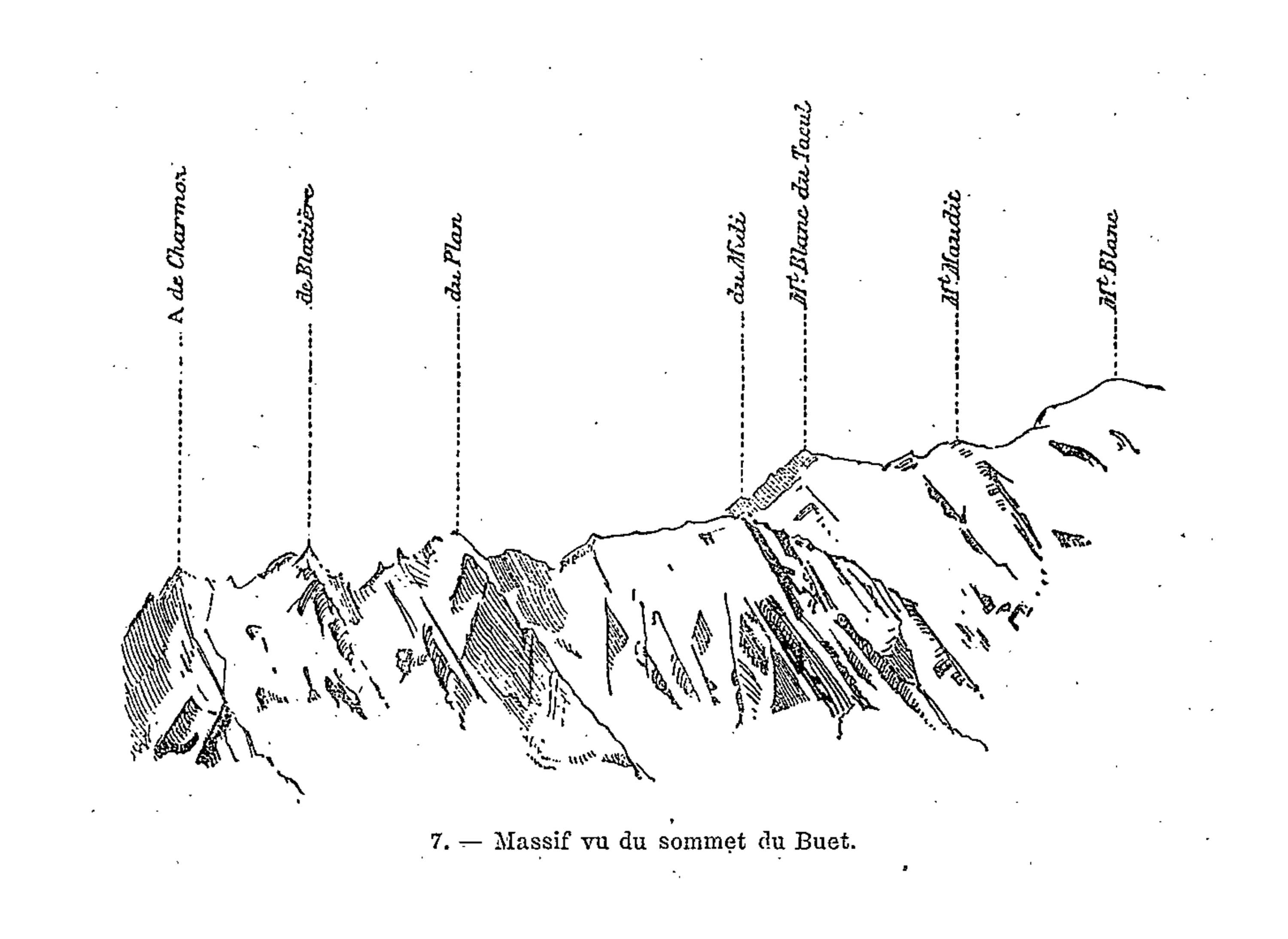
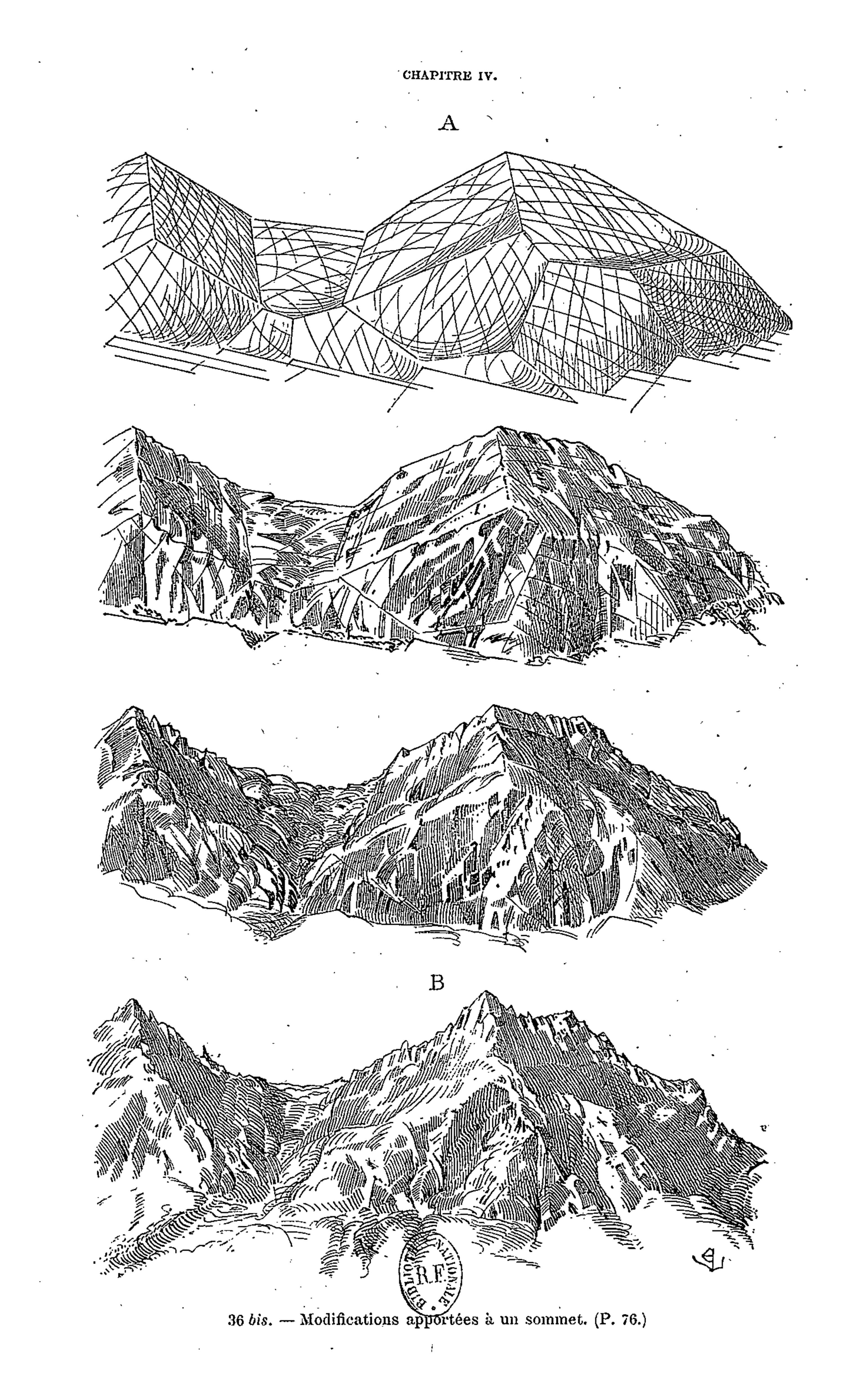
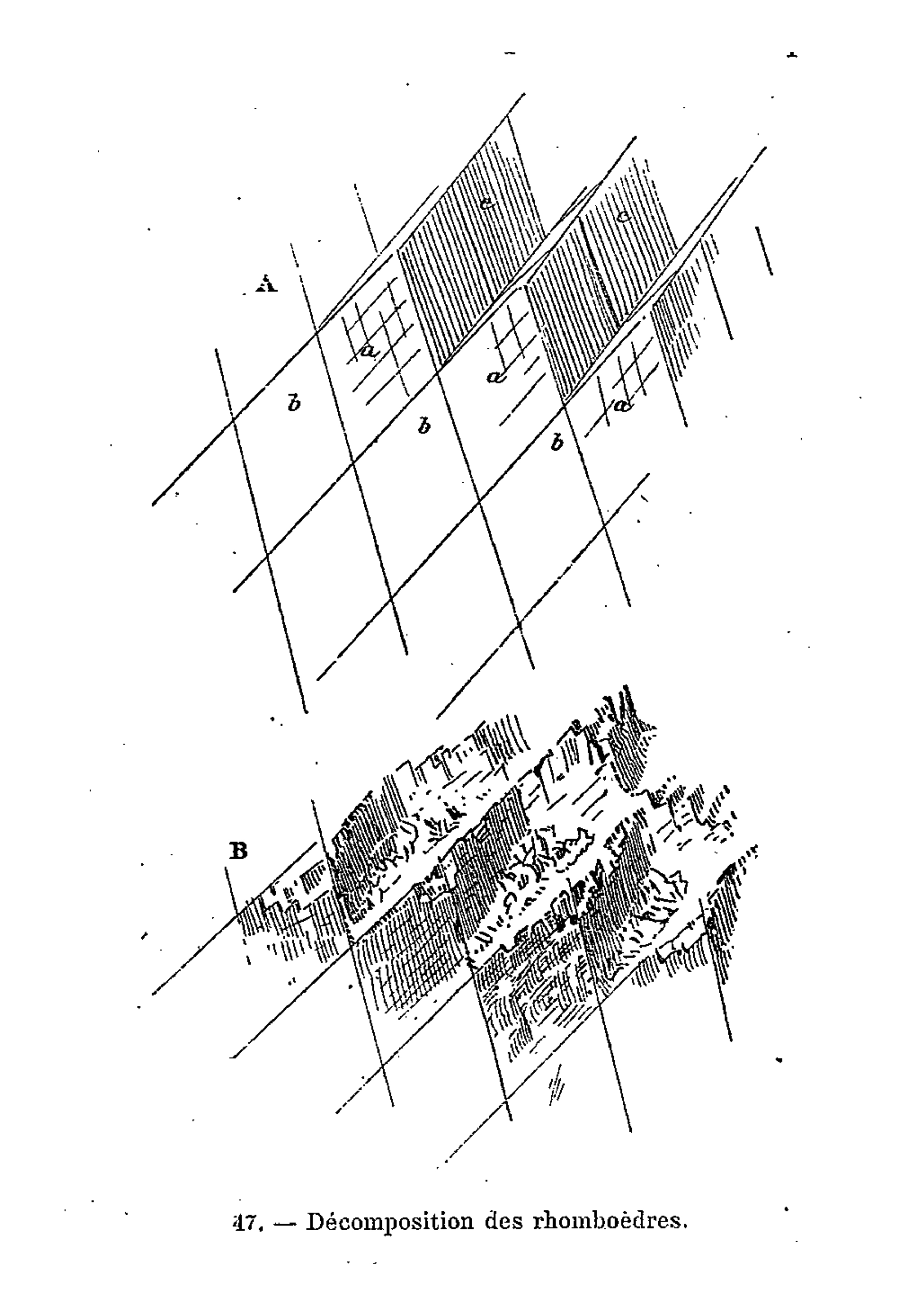
It is indeed from the close observation of the peaks and cols which make up the great massif that the highly pictorial form transformed, under Viollet-le-Duc’s wilful scrutiny, into a perfectly regulated crystalline system. In looking at these complex forms, we are taught to recognise a systematic, underlying order. But Viollet-le-Duc did not want to describe simply a static order. His Massif du Mont Blanc is primarily an attempt to reconstruct from the original upheaval, what, according to him, shaped the great massif over time. Once the primordial granitic mass crystallised under cooling, or metamorphosed under pressure, it underwent a rapid disintegration, the rhombohedral blocks splitting as water filtered through the interstices of lamination and expanded under frost, and as glaciers eroded the mass. But that very process of ruination is what best reveals the crystalline system. And what can be seen on a grand scale is repeated indefinitely in each of the masses, secondary, tertiary, and so forth.
Mont Blanc thus acts as one huge crystal formation, every edge, every peak and aiguille following a geodesic structure. This sort of unificatory explanation of natural phenomena did not belong only to Viollet-le-Duc. In fact, his geological ideas follow the general system of famous French geologist Léonce Élie de Beaumont (1798-1874), who devoted his life to proving that a unified geometrical network – the réseau pentagonal – organises the tectonics of the entire planet. But thanks to Viollet-le-Duc’s written and, especially, his visual language, we are made to witness more, as if the gigantic chaotic mass of the Mont Blanc was a deliberate construction, an architecture that can be restored to its rational idea. The two sketches that stand side by side on the drawing reproduced above, one a diagram, the other a rendering of ruined mountain peaks, is the illustration of a process of restoration. Viollet-le-Duc was explicit about the analogy between architecture and geology in the introduction to his Le massif du Mont Blanc:
“To analyse carefully a group of mountains, the manner in which they were formed, and the causes of their ruin; to discover the order in which the phenomena of upheaval occurred, the conditions in virtue of which they have resisted or endured the action of atmospheric agents, to note the chronology of their history, is to devote oneself to a work of methodical analysis which is, on a grander scale, analogous to that to which the practical architect and the archaeologist applies himself when drawing conclusions from the study of buildings.”









Lieu: Massif du Mont-Blanc, Alps
Collection: Ministère de la Culture - Médiathèque du Patrimoine, Dist. RMN-Grand Palais
Text: Martin Bressani, Eugène-Emmanuel Viollet-le-Duc, 2007
Publié: Avril 2018
Catégorie: Cartographie
Source